Is chili powder spicy?
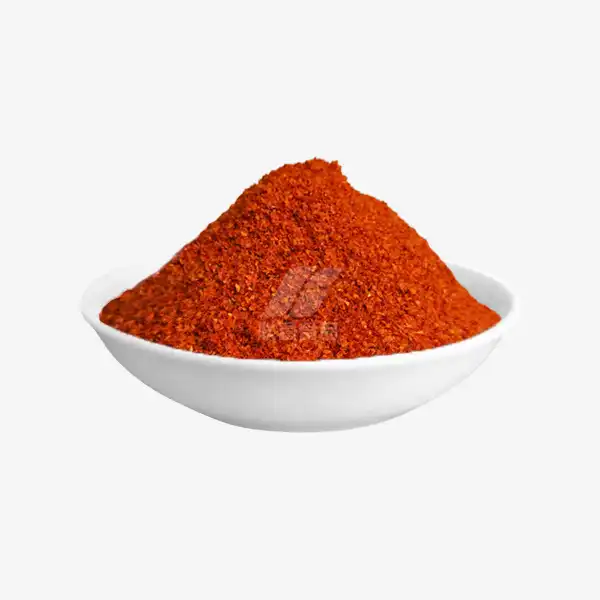
Chili powder is a versatile spice blend that adds depth and flavor to many dishes. But one question often arises: is chili powder spicy? The answer isn't as straightforward as you might think. Let's delve into the world of pure chili powder to uncover its heat levels, health benefits, and culinary uses.
Understanding the Heat in Pure Chili Powder
Pure chili powder, made from ground dried chili peppers, can pack quite a punch. However, its spiciness varies widely depending on the chili variety. Some types, like ancho or paprika, provide more flavor than heat, adding depth and smokiness. On the other hand, varieties like cayenne or habanero can bring intense heat, igniting your taste buds with their fiery kick. The level of spiciness is largely influenced by the specific chili used, offering a range from mild to extremely hot.
The Scoville scale, which measures the heat of peppers, provides insight into the potential spiciness of pure chili powders:
- Bell Pepper: 0 Scoville Heat Units (SHU)
- Ancho: 1,000-1,500 SHU
- Jalapeño: 2,500-8,000 SHU
- Cayenne: 30,000-50,000 SHU
- Habanero: 100,000-350,000 SHU
It’s important to distinguish that commercial "chili powder" typically contains a mix of spices like cumin, garlic powder, and oregano, which can mellow the heat. In contrast, pure chili powder is made exclusively from ground chili peppers, making it much spicier. The blend of additional spices in commercial versions helps balance the flavor, but if you're seeking a more intense heat, pure chili powder is the way to go.
Health Benefits of Pure Chili Powder
Beyond its fiery flavor, pure chili powder boasts numerous health benefits:
1. Metabolic Boost: Capsaicin, the active compound responsible for the heat in chili peppers, has been shown to increase metabolism. It can help the body burn more calories and aid in weight management by promoting fat oxidation and boosting thermogenesis, which is the process of heat production in the body.
2. Pain Relief: When applied topically, capsaicin can provide relief from certain types of pain. It works by desensitizing pain receptors and reducing pain signals sent to the brain. It’s commonly used in creams and ointments for conditions like arthritis, muscle pain, and neuropathic pain.
3. Antioxidant Properties: Chili peppers are a rich source of vitamins A and C, both of which are powerful antioxidants. These nutrients help neutralize free radicals in the body, protecting cells from oxidative damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
4. Heart Health: Some studies suggest that consuming chili peppers regularly may help reduce the risk of heart disease. Capsaicin may improve circulation, lower cholesterol levels, and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to better cardiovascular health.
5. Digestive Aid: Contrary to common belief, moderate consumption of chili can stimulate the production of digestive juices, potentially enhancing digestion. It can help with gastric motility and may even provide relief from indigestion or bloating.
While these benefits are promising, it's essential to consume chili powder in moderation, especially if you have a sensitive stomach or are prone to acid reflux.
How to Use Pure Chili Powder in Cooking?
Pure chili powder is a culinary powerhouse, capable of transforming bland dishes into flavor-packed delights. Here are some innovative ways to incorporate it into your cooking:
1. Spice Rubs: Chili powder makes an excellent base for creating a zesty rub for meats. Combine it with other spices like cumin, garlic powder, paprika, and a touch of brown sugar to create a flavorful seasoning that can be massaged into meats like chicken, beef, or pork. This spice blend enhances the flavor and adds a kick to your grilled or roasted dishes.
2. Soups and Stews: A pinch of chili powder can elevate the flavor profile of hearty soups and stews. Whether you’re making a chili, a vegetable soup, or a rich stew, adding chili powder brings depth, warmth, and a subtle heat that complements the other ingredients. It works particularly well in bean-based dishes, adding complexity to their flavor.
3. Marinades: Chili powder is a great ingredient for making flavorful marinades. Combine it with olive oil, vinegar, and herbs like oregano, thyme, or cilantro to create a marinade that can be used for vegetables, chicken, beef, or even tofu. The chili powder infuses the dish with heat and a smoky, savory undertone, making it a perfect addition to your grilling or roasting recipes.
4. Baked Goods: For a unique twist, try adding a small amount of chili powder to chocolate desserts or savory breads. A pinch of chili in chocolate cakes, brownies, or cookies can create a delightful contrast of heat and sweetness. It also works well in savory breads or cornbread, adding an unexpected kick that pairs perfectly with cheese or butter.
5. Homemade Hot Sauce: You can create your own custom hot sauce by blending pure chili powder with vinegar, garlic, and a pinch of salt. This simple combination can be adjusted to your taste, allowing you to control the heat level and flavor profile. Use it as a topping for tacos, grilled meats, or as a dipping sauce.
Conclusion
So, is chili powder spicy? The answer depends on the type of chili used and whether you're dealing with pure chili powder or a spice blend. Pure chili powder can range from mild to extremely hot, offering not just heat but also a wealth of health benefits and culinary possibilities.
At Xinghua Lianfu Food Co., Ltd., we specialize in producing high-quality dehydrated vegetables and spices, including various types of pure chili powder. Our products undergo rigorous quality control to ensure the highest standards of flavor and safety. For more information about our pure chili powder offerings, please contact us at qingzhengliu@jslianfu.com.
References
1. Johnson, A. (2021). "The Scoville Scale: Understanding Chili Heat". Journal of Culinary Science, 15(3), 145-160.
2. Smith, B. et al. (2020). "Health Benefits of Capsaicin: A Comprehensive Review". Nutrition Today, 55(2), 79-91.
3. Garcia, M. (2019). "Culinary Applications of Pure Chili Powder". International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science, 18, 100176.
4. Lee, Y. et al. (2022). "Metabolic Effects of Capsaicin Consumption: A Systematic Review". Metabolism, 128, 154950.
5. Brown, R. (2018). "The History and Cultural Significance of Chili Powder". Food, Culture & Society, 21(1), 1-19.

_1729843393550.webp)